
The dynamic nature of modern business ensures that change is the only constant, the latest of which sees organizations facing pressures to successfully navigate the digital disruption rippling across sectors.
In tandem with this sits evolving customer expectations, which continue to be a major motivator of businesses industry-wide as many undergo digital transformation (DX) to improve the delivery of their products and services.
Research shows over half of consumer companies are turning to artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to make their businesses more agile, and this is having a direct impact on the customer experience.
When customer satisfaction depends so heavily on the delivery of high-value products and services, continuously changing, improving, and iterating on your solutions becomes not just a choice but a business imperative.
Strategic change management emerges as the ideal solution for traversing these shifts, and some key change management positions act as levers for this process.
In wrapping up this article, our readers will comprehend the different roles within change management.
These roles are integral to managing, guiding, and shaping the change process, intertwining to form a cohesive unit that propels organizational transformation.
We’ll begin by discussing the significance of change for businesses, delve into the varied levels of change, outline roles and responsibilities, and examine the potential impact of change management in dynamic environments.
The importance of change management in today’s business arena

As businesses navigate an era defined by digital disruption and volatile market fluctuations, the ability to adapt effectively is no longer just an advantage—it’s key to prospective success.
Change management facilitates this adaptation, enabling organizations to transition smoothly from existing processes to innovative practices. It helps mitigate potential resistance, reduces operational disruption, and ensures change initiatives deliver their intended outcomes.
According to research by The Harvard Business Review, 2022 saw an increase in planned enterprise changes impacting the average employee. These changes, totaling around 10 per employee, ranged from restructuring efforts aimed at boosting efficiencies and cultural transformations designed to embrace new work methodologies to the phasing out of outdated technology systems.
In essence, change management connects strategic vision to operational reality. The vehicle allows businesses to transform their practices, enhance their performance, and ultimately thrive amidst the complexities of the modern business arena.
Understanding the Different Levels of Change Management
Change is a universal necessity that permeates various business verticals, each distinguished by its unique focus and strategies. Below we delve into the three primary levels of change management, offering insights to empower successful change initiatives.
- Enterprise Change Management Capability
Enterprise Change Management (ECM) Capability is an overarching framework permeating every organizational level. It’s about building and strengthening the organization’s ability to embrace change at a macro level. This involves creating a culture receptive to change, establishing procedures for managing change, and embedding change management practices into the company’s DNA.
ECM goes beyond dealing with individual changes. It enables a company to respond quickly to market shifts, regulatory changes, and technological advancements. A robust ECM capability can turn change from a disruptor into a competitive advantage, allowing businesses to adapt, innovate, and evolve in today’s fast-paced business environment1.
- Organizational Change Management
On the next tier, we have Organizational Change Management (OCM). Unlike ECM, which is broad and all-encompassing, OCM focuses on a specific organizational project or transformation. This could involve implementing a new technology, restructuring departments, or altering business processes.
OCM involves a series of steps, including assessing the need for change, developing a strategic plan, communicating the change, training employees, and monitoring the implementation. It’s about managing the human side of change, ensuring employees understand why change is necessary, how it impacts their roles, and what to do to adapt.
- Individual Change Management
Finally, at the most granular level, we have Individual Change Management. This level focuses on helping individuals within the organization navigate change. It recognizes that organizational change can only be successful if individuals successfully transition from current working methods to new ones.
Individual Change Management employs models like ADKAR (Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability, Reinforcement), which provide a roadmap for understanding and managing personal transitions. It involves communication, training, coaching, and support to help individuals understand the change, build their desire to participate and engage, gain the knowledge and abilities needed to change, and reinforce these changes to ensure they stick.
In conclusion, understanding these different levels of change management is crucial in crafting a comprehensive strategy that addresses change from a holistic perspective. By integrating and aligning these levels – the enterprise, the organization, and the individual – businesses can successfully navigate the complexities of change and emerge stronger and more resilient.
Change Management positions and responsibilities

Given the broad scope of organizational change, roles and titles within the change management field can greatly differ and may overlap based on the unique needs of each business.
In a general sense, those who help execute the change process include change managers, who oversee and implement the change strategies; change analysts, who assess the impact of changes and monitor their effectiveness and change champions, who act as advocates for change within the organization, to name a few.
These individuals work together to ensure a smooth transition from old processes to new ones, which involves facilitating a high standard of communication, collaboration, and education across the organization.
Let’s explore these positions further below, looking at the roles and responsibilities of those critical in ensuring the smooth transition between one state and another.
- Change Manager: The Change Manager is the ship’s captain when orchestrating organizational change. They lead the process by crafting comprehensive change management strategies that align with the organization’s goals. A significant part of their job description involves ensuring that changes are effectively communicated across all levels of the organization and understood and accepted. They act as a bridge between the executive vision and the operational implementation of that vision.
- Change Analyst: The Change Analyst is the navigator in the journey of change, providing valuable support to the Change Manager. They delve into the depths of proposed changes, analyzing and assessing their potential impact. Their role is akin to that of a detective, tracking changes and extracting data-driven insights that shape decision-making processes. Their analytical skills play a pivotal role in determining the course of action.
- Change Champion: Change Champions are the torchbearers of change within the organization. Regardless of their position in the company hierarchy, they are vital in promoting and facilitating change. Their job description involves kindling enthusiasm, fostering buy-in, and stimulating engagement among their peers. They advocate for change, inspiring others to embrace new ways of doing things.
- The Change Advisory Board: This group is the council of wisdom in change management. Comprising key stakeholders, the Change Advisory Board reviews and approves changes, ensuring minimal disruption and maximum alignment with business objectives. Their role is to provide oversight, offering a balanced perspective to ensure that change initiatives are in the organization’s best interest.
- The Change Process Owner: The Change Process Owner is the architect of the change process. They are responsible for setting the blueprint – defining and maintaining the change management process. Their role ensures that the process aligns with business needs and industry best practices, providing a robust framework for effectively managing change.
- Change Management Teams: These teams are the builders who bring the blueprints of change to life. Composed of various individuals, these teams execute the change plans, turning strategy into action. They collaborate closely with the Change Manager, Analysts, and Champions, playing a critical role in implementing change.
Change management additional roles and responsibilities
As previously stated, wide-reaching organizational change is not siloed and often requires leaders to advocate cross-collaboration between various departments and teams.
According to McKinsey, 70% of change programs fail due to a lack of engagement for leaders and employees.

Separate from leadership roles, we have technicians, for instance, who form the backbone of implementing technical changes. These individuals work closely with Change Management Teams to ensure seamless transitions during technological shifts.
We have IT support specialists who provide indispensable technical support during the change process. Leveraging their expertise, they help to mitigate technical issues and smoothen the transition, ensuring that all technical aspects of the change are handled effectively.
Operations Directors also play a crucial role, overseeing the operational aspects of change management. Their job is to ensure that day-to-day functions align with the new changes without hindering productivity, keeping the organization’s operations running smoothly even during times of transition.
Client Relations Managers also play a key role when communicating changes to clients. They manage client expectations and maintain strong relationships during the transition, ensuring the organization’s external relations remain solid despite internal changes.
Change management skills and requirements
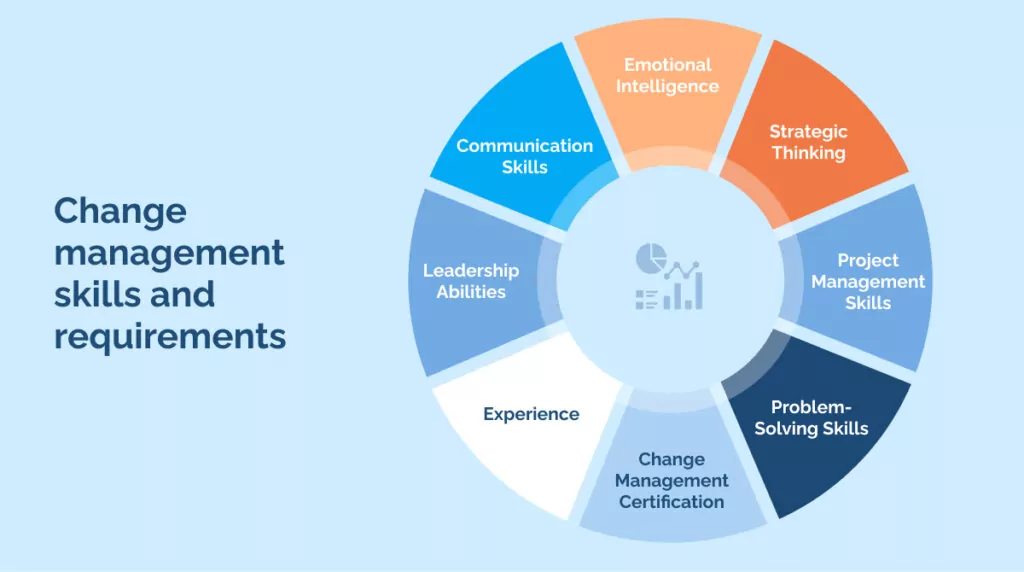
A unique blend of skills is required to navigate the multi-faceted field of change management transitions successfully.
Professionals in this field must be able to navigate the complexities of change, guiding teams and individuals through the process smoothly and effectively.
Here are some key change management skills and requirements that are essential for change management positions:
Leadership Abilities: Change managers should exhibit strong leadership qualities. They must inspire and motivate others, fostering a positive environment conducive to change. Leadership also involves making tough decisions, setting clear goals, and ensuring the team is aligned with the organization’s vision.
Communication Skills: Excellent communication is paramount in change management. Change managers must articulate the need for change, its benefits, and how it will be implemented. They should be adept at communicating with various stakeholders, from top executives to front-line employees.
Emotional Intelligence: Change can evoke emotions in employees, from fear and resistance to excitement and enthusiasm. Change managers need high emotional intelligence to understand and manage these emotions, helping employees navigate the change process.
Strategic Thinking: Change managers need to be strategic thinkers. They should be able to envision the big picture, identify potential obstacles, and devise effective strategies to overcome them. This includes understanding the organization’s culture, processes, and structures and how the proposed change might impact them.
Project Management Skills: Implementing change is often a project in itself. Therefore, change managers should possess project management skills to successfully plan, execute, monitor, and close change initiatives.
Problem-Solving Skills: Unexpected issues often arise during the change process. Change managers should have strong problem-solving skills to identify these issues and develop practical solutions.
Change Management Certification: Many employers prefer candidates with a certification in change management. The Prosci Change Management Certification and the Certified Change Management Professional (CCMP) certification are two widely recognized credentials in the field.
Experience: Practical experience managing change projects is highly valued. This experience can provide a hands-on understanding of the dynamics of change within an organization and the best ways to facilitate it.
To summarise, change management positions require a mix of interpersonal, strategic, and technical skills. Professionals can lead their organizations toward a future-ready state by developing these competencies.
The Impact of Effective Change Management on Business Success

With 47% of organizations more likely to meet their objectives when integrating change management than the 30% that do not, change management emerges as a key enabler of success—fostering adaptability and resilience in the face of constant flux.
Exploring the roles, skills, and requirements of change management positions throughout this article, it’s evident that these key players are instrumental in driving the change management process and wider strategic transformations.
According to Gartner, the typical organization has undertaken five major firmwide changes in the past three years, and nearly 75% expect to multiply the types of major change initiatives.
As we advance into the future, the complexity of contemporary organizations is expected to amplify. Change practitioners must gear up for this inevitability, ensuring they are fully prepared to steer their companies through any transformations, irrespective of their magnitude.
According to McKinsey, a transformation is 5.8 times more likely to be successful at organizations where CEOs communicate a compelling, high-level change story.
For those tasked with affecting change, research has identified understanding the external environment, preparing for change, and having a consistent message as common success factors.
Change leaders embodying these key competencies, in tandem with a blend of strategic insight, proactive leadership, and robust execution, will ultimately cultivate a foundation in which change is met with minimal disruption and resistance.
WalkMe Team
WalkMe spearheaded the Digital Adoption Platform (DAP) for associations to use the maximum capacity of their advanced resources. Utilizing man-made consciousness, AI, and context-oriented direction, WalkMe adds a powerful UI layer to raise the computerized proficiency, everything being equal.



