The change process is a systematic approach to managing the transition from a current state to a desired future state.
It involves identifying, prioritizing, and implementing changes to improve organizational performance, enhance efficiency, or adapt to new circumstances.

According to Gartner, 73% of employees affected by change report moderate to high levels of stress. This stress, tied to change, results in a performance dip of 5% compared to their average-performing peers.
The change process becomes even more crucial for businesses in the high-octane digital era. The ability to change enables them to adapt to new technologies, market dynamics, and customer expectations, ensuring their survival and growth in the competitive business arena.
The digital realm is characterized by constant innovation and disruption. Without a well-managed change process, businesses risk falling behind, becoming obsolete, or failing to capitalize on new opportunities.
Spotting and putting into action key shifts is essential for competing in diverse markets. This could involve bringing on board state-of-the-art software, reworking tried-and-true operational methods, or shifting the very ethos of the organization.
In this piece, we will explore the change process – understanding its essence and establishing its importance for businesses – most notably those concentrating on digital transformation. Additionally, we will shed light on the benefits it offers and guide you through a comprehensive five-step implementation procedure to effectively embrace this change.
What Is the Change process?

The change process refers to the planned sequence of actions that an organization follows to transition from its existing operations to a more desired or optimal state.
This methodology is designed to enhance performance metrics, streamline efficiency, and enable adaptation to evolving circumstances.
Pivotal to this process is the identification of areas necessitating change. This could include technological upgrades, procedural modifications, or organizational cultural shifts. Following identification, these changes are prioritized based on their potential impact and feasibility, ensuring the most beneficial alterations are implemented first.
Implementation of these changes is guided by strategic planning and project management principles. It often involves stakeholder engagement, resource allocation, risk assessment, and continuous monitoring to ensure the change objectives are met effectively and efficiently.
The change process also includes mechanisms for feedback and learning.
Post-implementation reviews are conducted to assess the outcomes of the change initiatives, learn from the experience, and make necessary adjustments for future change processes.
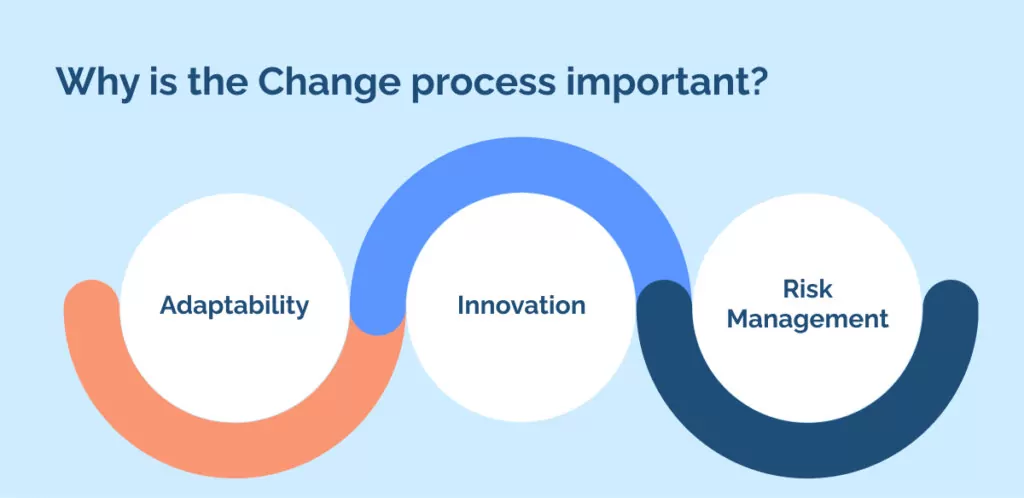
Why is the Change process important?
The change process fosters business resilience. Companies are equipped to navigate unforeseen challenges and fluctuations, ranging from cybersecurity threats to abrupt market shifts. This approach also promotes a culture of perpetual learning and growth, crucial in the digital era, where customer demands and technological advancements constantly evolve.
Additionally, the change process aids in successfully implementing digital transformation strategies. It ensures that changes are not just superficial but deeply ingrained within the organization’s structures, systems, and culture.
This way, businesses can fully harness the power of digital technologies, driving improved performance, efficiency, and customer engagement.
Below we further explore the multifaceted benefits of a well-orchestrated change process, highlighting its pivotal role in steering organizational growth and resilience in an increasingly dynamic business ecosystem.
Adaptability: The dynamic world of business demands adaptability. The change process equips organizations with the tools to respond efficiently to shifts in market conditions, technological advancements, and changes in consumer behavior.
This continuous reassessment and realignment of operations ensures businesses maintain their competitive edge. The change process facilitates smooth internal transitions, such as organizational restructuring or policy updates, minimizing operational disruptions.
Innovation: The change process acts as a springboard for innovation. It encourages the ongoing exploration of new ideas and the refinement of existing processes, products, or services.
A structured approach to implementing innovative solutions provided by the change process enables businesses to differentiate themselves, stay at the forefront of their industry, and deliver exceptional value to their customers.
Risk Management: A risk management framework is another crucial aspect where the change process plays a vital role. It assists in identifying potential risks associated with any change at an early stage and aids in formulating effective mitigation strategies.
Comprehensive risk assessments, implementation of robust controls, and contingency planning are all part of this process. Proactive risk management minimizes disruptions, reduces costs, safeguards reputation, and builds organizational resilience, allowing businesses to recover quickly from setbacks and navigate challenges with greater ease.
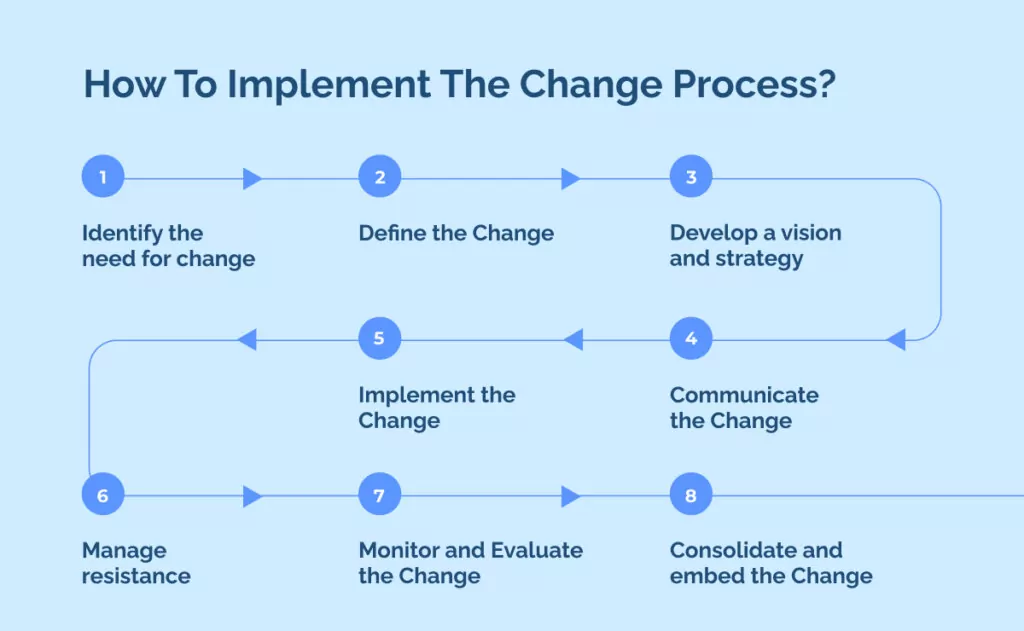
How To Implement The Change Process?
The change process needs to be tailored to the organization’s specific needs. There’s no use implementing an off-the-shelf solution; it should be tailored to fit the organization’s unique context and objectives.
Here are some steps to consider when rolling out a change process:
- Identify the need for change
A shift in strategy becomes essential when an organization faces challenges in its current operations or market conditions.
This step thoroughly examines internal processes, performance data, and market trends. It’s about spotting gaps, addressing weaknesses, and capitalizing on opportunities.
The process needs to be data-driven, involving careful analysis of metrics and KPIs. The organization can ensure it remains competitive and relevant by identifying areas needing change.
- Define the Change
Defining the change is a pivotal step in the transformation process.
This involves detailing the scope, objectives, and potential impact of the proposed changes on various facets of the organization.
A clear definition helps set expectations, reduce uncertainty, and plan effectively. It establishes a clear path from the current state to the intended future state, creating a roadmap everyone can follow.
- Develop a vision and strategy
Creating a compelling vision and robust strategy sets the pace for the change process.
The vision presents a picture of what the future will look like post-change, serving as both a guide and a source of motivation.
The strategy provides a detailed action plan outlining the steps to be taken, resources needed, and potential roadblocks. It serves as a blueprint for achieving the vision, aligning all efforts towards a common goal.
- Communicate the Change
Communication plays a crucial role in any change management process.
It involves keeping stakeholders informed about the reasons for change, its benefits, and how it will be implemented. Consistent, transparent communication can help dispel fears, build trust, and secure buy-in from all involved.
Through effective communication, organizations can promote understanding, alleviate concerns, and foster a culture of cooperation.
- Implement the Change
The implementation phase is where plans turn into action.
It could involve introducing new technologies, altering business processes, or restructuring teams. Effective project management is vital during this stage to ensure tasks are completed as planned and disruptions are minimized.
Regular checks and balances ensure the implementation stays on track and any deviations are promptly corrected.
- Manage resistance
Resistance to change is a natural human response, often stemming from fear or discomfort.
The key to managing resistance lies in understanding its root causes and addressing them through empathy, support, and reassurance. Providing necessary training and resources can also help ease the transition.
Proactively dealing with resistance smoothens the change process and fosters a positive work environment.
- Monitor and Evaluate the Change
Post-implementation, monitoring the progress, and evaluating the effectiveness of the change is crucial.
This involves assessing whether the change has met its objectives, tracking key performance indicators, and gathering feedback.
Regular reviews and evaluations help identify areas for improvement and provide insights for future change initiatives.
- Consolidate and embed the Change
The final step in the change process is integrating the change into the organization’s everyday operations and culture.
This involves reinforcing the change through ongoing training, communication, and recognition. It ensures the sustainability of the change and its continued contribution to the organization’s success.
Making the change part of the organization’s DNA becomes a stepping stone to further growth and innovation.
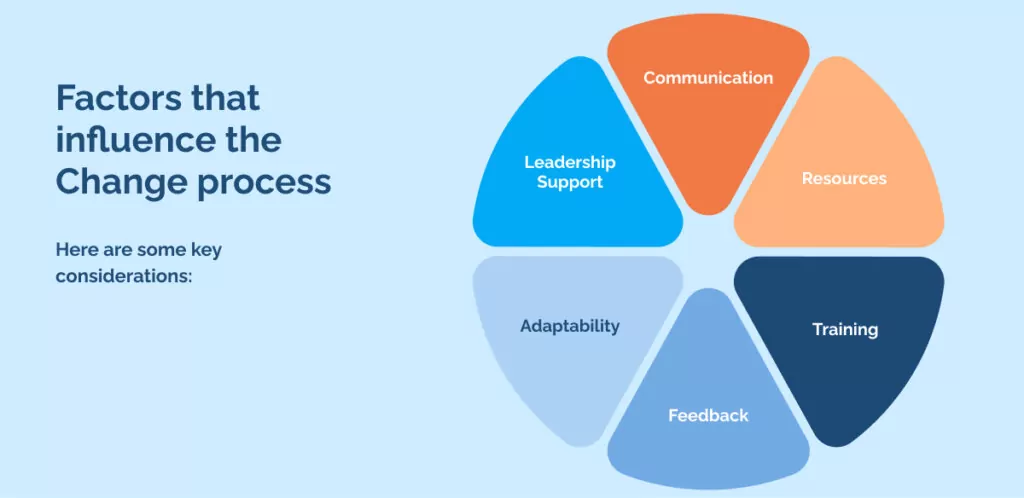
Factors that influence the Change process
The success of a change process greatly depends on its implementation.
Several factors can affect how smoothly and successfully a change is implemented, ranging from organizational culture to the availability of resources.
Here are some key considerations:
Leadership Support: Leadership needs to be committed to and actively involved in the transformation process for success. Leaders must demonstrate a clear vision, provide resources and support, and be willing to take risks. By setting an example of change readiness, they can help create a culture that supports transformation initiatives.
Communication: A significant part of the change process is communication. Organizations must communicate the need for change, objectives, and expected outcomes to stakeholders. Regular updates must be provided throughout the process to keep everyone informed and on track. Effective communication fosters understanding and garners support for the proposed changes.
Resources: Having enough resources is essential for successfully implementing a change process. Organizations need to assess their capacity in terms of human resources, technology, budgeting, and other areas before embarking on a transformation journey. Businesses can outsource specific tasks or hire experts to ensure completion within the required timeline.
Training: Organizations must provide training to employees at all levels to implement positive change. Training helps employees become familiar with the changes, understand their implications, and develop the skills needed to carry them out. It also ensures that everyone is equipped to use new systems, processes, and technologies efficiently during and after the process.
Feedback: Gathering feedback from stakeholders at various stages of a change process is essential for ensuring its effectiveness. Organizations need to solicit input from all involved, including employees, customers, and other stakeholders. This helps identify areas where the process can be improved and ensure everyone’s needs are met. Analyzing this data can also present valuable insights for future initiatives.
Adaptability: Change processes involve continuous learning and improvement. Organizations must be prepared to adjust their strategies according to stakeholders’ changing needs to ensure the initiative’s long-term success. Recognizing, analyzing, and responding quickly and appropriately to external factors is key for organizations navigating a dynamic environment.
What Comes After The Change Process?

Once a change process has been successfully implemented, businesses can anticipate a period of stabilization and potential growth.
The newly adopted practices, systems, or structures start to take root, gradually becoming the norm. During this phase, businesses often experience heightened efficiency and productivity as the adjustments made during the change process begin to show results.
Post-change, it’s crucial for businesses to maintain a culture of learning and development. Even after successful implementation, organizations should stay open to further adjustments based on feedback and performance data. This ensures that the changes continue to meet the organization’s learning curve goals and keep pace with any external shifts in the market or industry.
After the change process, businesses have the opportunity to evaluate their change management capabilities. Reflecting on what worked well and what could be improved provides valuable insights for future change initiatives. These insights can help refine the organization’s approach to change, making it more effective and less disruptive.
To conclude, successful change implementation also provides recognition and celebration opportunities. Acknowledging the efforts of all involved boosts morale and reinforces the most poignant aspects of the change.
WalkMe Team
WalkMe spearheaded the Digital Adoption Platform (DAP) for associations to use the maximum capacity of their advanced resources. Utilizing man-made consciousness, AI, and context-oriented direction, WalkMe adds a powerful UI layer to raise the computerized proficiency, everything being equal.



