
Macro trends such as talent disruption, inflation, skills shortages, and global tension have followed in the wake of the pandemic, according to LinkedIn’s 2023 Workplace Learning Report.
With the demand for new skills increasing, the report also finds that 89% of L&D pros agree that proactively building employee skills for today and tomorrow will help navigate the evolving future of work.

As such, microlearning is emerging as a preferred methodology for meeting the needs of twenty-first-century workers and contemporary businesses’ needs. The flexibility, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness of microlearning make it an ideal solution for organizations looking to develop a more agile and adaptive workforce.
By leveraging microlearning as a powerful employee development tool, L&D leaders can better facilitate organizational development, create a culture of continuous learning and support wider change management initiatives.
Research from Gallup reveals that only 21% of employees are engaged at work, and 33% of employees are thriving in their overall well-being.
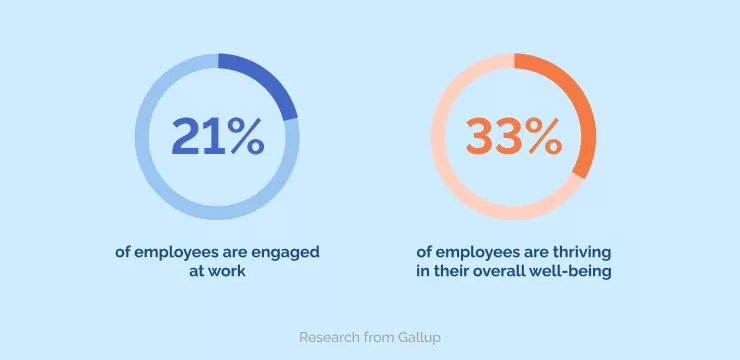
Embracing this contemporary methodology can improve productivity, engagement, retention, and business performance while acquiring the skills needed to drive business velocity.
Similarly, Microlearning’s on-demand accessibility and bite-sized format make it a great solution for busy workers seeking to balance their work and personal lives, as it allows them to learn at their own pace and schedule while still meeting their job demands.
This article delves into the concept of microlearning, examining its potential to enhance employee productivity significantly. We begin by demystifying microlearning and highlighting its many benefits, including increased knowledge retention and engagement. Alongside these advantages, we also address the challenges associated with implementing microlearning in a workplace setting, providing practical strategies for overcoming them.
To inspire and inform, we showcase four real-life microlearning examples from organizations that have leveraged this approach to achieve impressive results. We’ll conclude with a set of best practices for organizations seeking to implement their microlearning initiatives and unlock their workforce’s full potential.
What is microlearning?
Microlearning is an innovative learning approach that involves breaking down complex subjects or skills into smaller, more digestible pieces of information.
By breaking down complex topics into smaller, easily digestible chunks, microlearning allows employees to learn at their own pace and schedule. This approach enhances knowledge retention and improves engagement among employees who might feel overwhelmed or disengaged by traditional training methods.
SHRM found that when it comes to learning methods, organizations should consider employee preferences. The most favored options are online/self-paced courses (70%), online/instructor-led training (63%), in-person learning with an instructor (63%), and hybrid educational offerings (62%).

SHRM states: “The bottom line is that organizations should understand and attempt to meet the training needs and desires of their workforce with respect to the content, timing, and delivery of training,”
Benefits of microlearning
Training methods such as microlearning not only help employees acquire new skills and knowledge but also boosts morale, motivation, and job satisfaction.
Below, we will explore some key benefits of employee training and development programs for individuals and organizations.
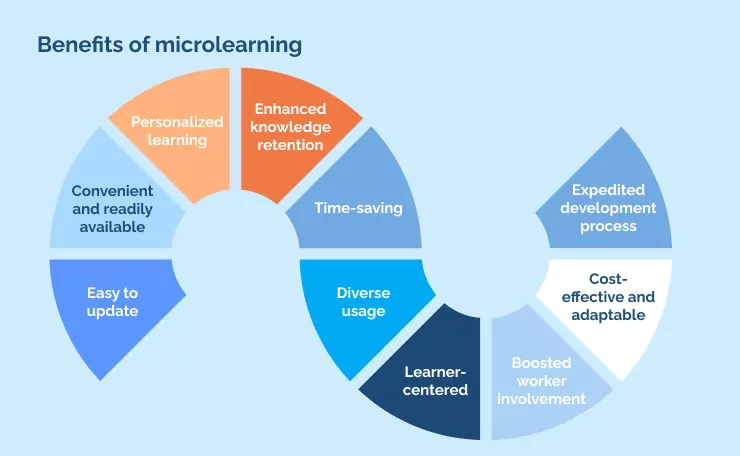
Easy to update: Microlearning courses are shorter and focused on specific topics, making them easier and quicker to update when compared to traditional training methods. This allows organizations to keep their training programs relevant and up-to-date with the latest information and trends.
Convenient and readily available: Microlearning enables learners to access training materials from anywhere and at any time, using a range of devices such as mobile phones, tablets, or laptops. This makes it a convenient and accessible learning method for busy employees.
Personalized learning: Microlearning allows learners to choose their learning path and pace, providing an individualized and customized learning experience that caters to their unique needs and preferences.
Enhanced knowledge retention: Microlearning is designed to deliver information in smaller, more digestible chunks, making it easier for learners to retain and recall the information over time. This results in improved knowledge retention and better performance outcomes.
Time-saving: Microlearning is a time-efficient training method that allows learners to complete courses quickly and without disrupting their work schedules. This results in less time spent away from work and increased productivity.
Diverse usage: Microlearning can be used for a variety of training purposes, including onboarding, compliance training, skill development, and leadership training. This makes it a versatile training method that can be applied across different industries and job roles.
Learner-centered: Microlearning puts the learner at the center of the training experience, allowing them to take charge of their learning journey and gain new skills in a way that works best for them.
Boosted worker involvement: Microlearning encourages active participation and engagement among learners, resulting in increased motivation, confidence, and job satisfaction.
Cost-effective and adaptable: Microlearning is a cost-effective training method that allows organizations to deliver high-quality training to a large number of learners without breaking the bank. It also adapts to changing business needs and can be updated quickly and easily.
Expedited development process: Microlearning courses have a shorter development cycle when compared to traditional training methods, allowing organizations to create and deliver training content quickly and efficiently.
Challenges of microlearning
The benefits from microlearning may be numerous, but organizations may face similar challenges when implementing this training approach.
Below we address some common challenges that organizations may encounter when implementing microlearning.
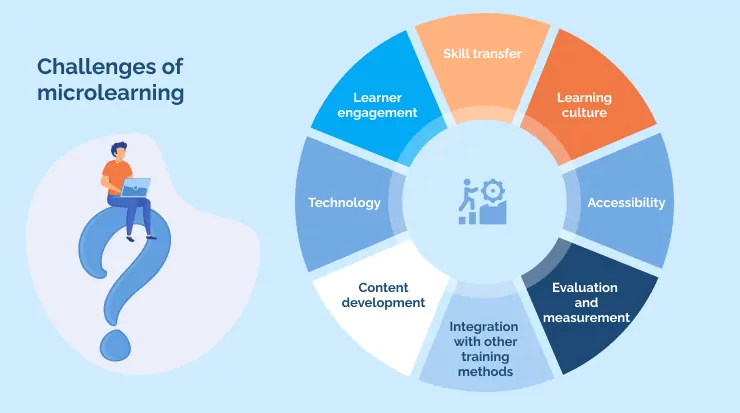
Content development: Creating effective microlearning content requires careful planning and design, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Technology: Implementing microlearning requires the right technology resources to facilitate training content delivery, tracking, and measurement. This impedes progress for organizations that do not have the necessary resources or expertise.
Learner engagement: Keeping learners engaged and motivated can be another obstacle when delivering short and focused microlearning modules, especially if they are not designed to be interactive or gamified.
Skill transfer: Ensuring that learners are able to apply the skills and knowledge acquired through microlearning in a real-world setting can prove difficult, especially if the training is not contextualized or followed up with appropriate reinforcement.
Learning culture: Incorporating microlearning into an organization’s learning culture can be taxing, especially if there is resistance to change or a lack of stakeholder buy-in.
Accessibility: Microlearning needs to be accessible to all employees, regardless of their location, schedule, or device preferences. Ensuring that the training is available and easily accessible to everyone can be a challenge.
Evaluation and measurement: Measuring the effectiveness of microlearning can be another difficulty, especially if the training is not tied to specific learning objectives or outcomes.
Integration with other training methods: Microlearning needs to fit seamlessly with an organization’s larger training and development strategy. Integrating microlearning with other training methods can feel like treading unfamiliar ground, especially if the existing training approach is more traditional or instructor-led.
Microlearning examples
This section will explore four real-life examples of organizations that have adopted microlearning and achieved impressive results.
These examples illustrate the versatility and effectiveness of microlearning as a training approach and can inspire organizations looking to implement microlearning into their training programs.
- Bosch Leverages On-Demand Microlearning

Bosch is a globally leading technology and engineering company most well-known for its innovative mobility, energy, and industry solutions.
With a reported employee count of over 421,338 in 2021, Jane Tham’s responsibilities as HR director for the company’s Singapore-based Southeast Asia division primarily included being a digital knowledge advocate within the organization.
By leveraging an on-demand modular method to microlearning, L&D leaders can “help to keep productivity at its optimum and yet cater to the short attention spans that we have now,” says Tham.
Bosch has demonstrated an openness to contemporary forms of L&D by offering its employees exclusive modules and training programs through a learning experience platform that they can access whenever and wherever they want.
Bosch is shifting from conventional in-person, lengthy seminars to providing users with bite-sized “nuggets of information” for more effective learning.
“Putting fun in learning is also important, which is why gamification is huge here at Bosch. And, of course, we believe in bite-sized and mobile learning – and this is where our e-university plays its part,” says Tham.
- IBM leveraging a Digital Adoption Platform (DAP) to improve onboarding experiences and poor user adoption rates

After transitioning to a cloud-based platform offering a range of digital products and expanding its scope to include cognitive solutions, IBM encountered a significant issue: user abandonment.
Customers were leaving due to inadequate onboarding experiences and the absence of accessible support.
To remedy this, IBM tapped into the microlearning features of WalkMe’s Digital Adoption Platform (DAP) to aid user onboarding and feature adoption of their bleeding-edge offerings.
Leveraging WalkMe’s Digital Adoption Platform (DAP), IBM provided a simplified, user-friendly experience that addressed the needs of its customers. Central to this was the incorporation of microlearning, which allowed for the quick and easy delivery of information in bite-sized chunks.
As a result of this approach, IBM saw impressive improvements in user retention rates, soaring from 50% to over 70%
“We knew that if we helped users reach ‘wow moments,’ those users would be much likelier to understand our product’s value and differentiation and ultimately subscribe,” says IBM’s former Chief Digital Officer and VP for Digital Transformation Nilanjan (Neel) Adhya.
- Unilever embraces gamification and “snackable” L&D.

With 148,000 employees, Unilever is a British-Dutch multinational consumer goods company that dates back over a century. The company boasts hundreds of brands, including popular household names like Axe, Dove, Lipton, and Knorr.
Despite demonstrating a knack for organizational agility and innovation throughout its almost ninety years in business, Unilever continues revitalizing all workforce areas through continuous change-management-led learning and development (L&D) initiatives.
Unilever launched its Future of Work initiative, a wide-scoping plan to build up digital readiness within the workforce for an increasingly digitalized and automated era. Goals within the initiative included “accelerating the speed of change within Unilever, reskilling staff through a culture of life-long learning, and adopting flexible work practices.”
Unilever’s Future of Work initiative centered on three pillars:
- accelerating the speed of change
- accessing mission-critical skills now and in future
- Increasing flexibility through new employment models
Unilever invested heavily in training and development in 2022, spending €77 million on upskilling its workforce. On average, each employee received 27 hours of training and development, with an estimated €644 invested per employee. The company also focused on equipping employees with future-fit skills, reskilling, or upskilling 15% of its workforce in data science, agile working, and digital manufacturing expertise to drive business growth.
Tasked with consolidating Unilever’s Future of Work initiative into a single systematic operation, former CHRO Leena Nair shared via Forbes, “At Unilever, we talk about snackable learning, or little and often, because, as a society, our ability to focus on tasks has reduced over the years.”
“So all of our learning is underpinned by what we call curiosity and focus. Invest 15 minutes a day in a TED talk or having a coffee with a colleague to keep your skills sharp. When you feel capable, you can thrive, so learning is the essence of thriving,” she continues.
As one of their many solutions for capturing and embracing digital disruption across sectors, Unilever is building employees’ expertise in data acquisition and analytics with its Digital Factory Programme, cultivating skills essential to operate its increasingly sophisticated factories.
Unilever is also adopting a microlearning-based approach to employee training, using gamification strategies to engage engineering teams and boost their technical skills. By breaking down training content into small, easily-digestible modules, Unilever aims to increase retention rates and provide more targeted learning opportunities.
- ConnectWise utilizes bespoke micro-courses

ConnectWise is an IT solutions company that helps Managed Service Providers (MSPs) upskill teams and empower help desk technicians and new hires to incorporate learning in their workflow.
ConnectWise needed to develop contemporary training programs to meet industry requirements better and reduce key skills gaps within the dynamic IT arena.
ConnectWise has reduced onboarding time for new employees by utilizing the 360 Learning platform. The company can seamlessly incorporate on-demand training into workflows without hindering productivity through this platform. This approach ensures that new hires receive the necessary training they need while allowing them to get up to speed with their regular tasks quickly.
By consolidating all training resources and materials within the learning platform, L&D teams could deliver bespoke, targeted training courses within two weeks.
It would previously take “anywhere from a month to two months” to develop training programs and set up a course, whereas now it can take just 1-2 weeks to build, ship, and update modules.
ConnectWise is a prime example of how microlearning has transformed employee training. Rather than pulling technicians from the floor for hours, ConnectWise can now offer courses that take just a few minutes to complete.
“And then they can get right back into the action,” says Lee Savage, Help Desk Trainer at ConnectWise.
“The thing that I think we all here at ConnectWise love about 360Learning is the connectivity,” says Lee. “Getting people together. Allowing them to interact.”
ConnectWise’s technicians can also stay connected to forums that discuss best practices and product improvements through IT Nation meetings, available as on-demand video presentations. This new method of engagement enables employees to access important information and connect with industry experts at their convenience without disrupting their regular work schedules.
ConnectWise also deployed on-demand upskilling learning opportunities via mobile apps. Their employees can participate in micro-courses on their mobile devices, whether at home, during a commute, or between customer calls.
In addition, nascent microlearning methods have enabled the following:
- Their average training module length was reduced to 12 minutes compared with 30 minutes via their previous LMS.
- x 2 employee adoption of 360Learning vs. previous LMS
- They also have a faster learning-to-use ratio, meaning technicians implement what they have learned directly into play.
- Technicians spend more time taking phone calls or chats thanks to shorter training sessions.
Microlearning Best Practices
Organizations need to follow some best practices to ensure the success of microlearning programs.
LinkedIn’s 2019 Workplace Learning Report shows “Talent developers only spend 15% of their time promoting employee engagement with learning.”
Organizations should align their microlearning initiatives with their training strategy and business goals. This means carefully considering the skills and knowledge that employees need to acquire and designing microlearning modules that address those specific needs.
Additionally, organizations should use engaging and interactive formats to keep learners motivated and involved and incorporate opportunities for reinforcement and practice to ensure that learning is transferred to the workplace.
Organizations should also leverage technology effectively to deliver and track microlearning content. This includes using LMS or other technology platforms to deliver training content, track learner progress, and provide analytics for evaluation and continuous improvement.
Incorporating microlearning into an organization’s training and development approach can be a valuable tool for navigating the tumultuous business landscape. With the Covid-19 pandemic and wider macroeconomic uncertainties, businesses must be agile and adaptable to succeed in this environment.
As we move towards a more digital and dynamic future, Microlearning presents a flexible and scalable approach to employee training that may potentially play a crucial role in shaping the workforce of tomorrow.
WalkMe Team
WalkMe spearheaded the Digital Adoption Platform (DAP) for associations to use the maximum capacity of their advanced resources. Utilizing man-made consciousness, AI, and context-oriented direction, WalkMe adds a powerful UI layer to raise the computerized proficiency, everything being equal.



